mohmedxpmpa
الجمعة، 20 مايو 2011
شبكه و منتديات اوكشن
السبت، 26 يونيو 2010
Personal computer hardware
personal computer is made up of multiple physical components of computer hardware, upon which can be installed an operating systemand a multitude of software to perform the operator's desired functions.
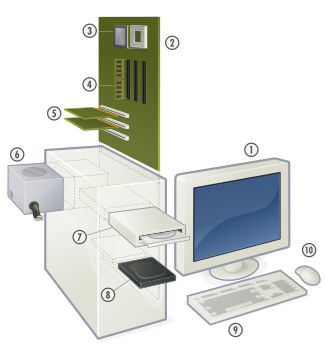
1. Monitor
2. Motherboard
7. Optical disc drive
9. Keyboard
10. Mouse

Though a PC comes in many different forms, a typical personal computerconsists of a case or chassis in a tower shape (desktop), co
Motherboard
The motherboard is the main component inside the case. It is a large rectangular board with integrated circuitry that connects the rest of the parts of the computer including the CPU, the RAM, the disk drives (CD, DVD, hard disk, or any others) as well as any peripherals connected via the ports or the expansion slots.
Components directly attached to the motherboard include:
- The central processing unit (CPU) performs most of the calculations which enable a computer to function, and is sometimes referred to as the "brain" of the computer. It is usuallycooled by a heat sink and fan.
- The chip set mediates communication between the CPU and the other components of the system, including main memory.
- RAM (Random Access Memory) stores all running processes (applications) and the current running OS.
- The BIOS includes boot firmware and power management. The Basic Input Output System tasks are handled by operating system drivers.
- Internal Buses connect the CPU to various internal components and to expansion cards for graphics and sound.
- Current
- The north bridge memory controller, for RAM and PCI Express
- PCI Express, for expansion cards such as graphics and physics processors, and high-end network interfaces
- PCI, for other expansion cards
- SATA, for disk drives
- The north bridge memory controller, for RAM and PCI Express
- Obsolete
- Current
- External Bus Controllers support ports for external peripherals. These ports may be controlled directly by the south bridge I/O controller or based on expansion cards attached to the motherboard through the PCI bus.
[edit]Power supply
A power supply unit (PSU) is the component that supplies power to the other components in a computer. More specifically, a power supply unit is typically designed to convert general-purpose alternating current (AC) electric power from the mains (100-127V in North America, parts of South America, Japan, and Taiwan; 220-240V in most of the rest of the world) to usable low-voltage DC power for the internal components of the computer. Some power supplies have a switch to change between 230 V and 115 V. Other models have automatic sensors that switch input voltage automatically, or are able to accept any voltage between those limits. It converts high voltage into low voltage.
Power supply units often used in computers are SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply). The SMPS provides +12, -12, +5, -5 and 3.* DC Volts for operation. When using the SMPS, it results in uninterrupted output within a wide range of input AC voltages. SMPS makes the power supply unit compact, rigid and reliable. The SMPS will switch over until it gets a negative loop from the computer's motherboard when switching ON the CPU. First, the SMPS converts the input AC voltage into corresponding DC voltage, which is then applied to a switching circuit at very high frequency. This high frequency (AC) is fed to a step down transformer with different tapings for various voltages required to run a computer. These AC voltages are then rectified and filtered. Finally, we get pure DC voltage of different levels.The power supply he si main of motherbord and then current motherbord for fan, process and SMPS of name hard wire of smps wire and power managment of process fan and other devisec of power supply
[edit]Removable media devices
- CD (compact disc) - the most common type of removable media, suitable for music and data.
- CD-ROM Drive - a device used for reading data from a CD.
- CD Writer - a device used for both reading and writing data to and from a CD.
- DVD (digital versatile disc) - a popular type of removable media that is the same dimensions as a CD but stores up to 12 times as much information. It is the most common way of transferring digital video, and is popular for data storage.
- DVD-ROM Drive - a device used for reading data from a DVD.
- DVD Writer - a device used for both reading and writing data to and from a DVD.
- DVD-RAM Drive - a device used for rapid writing and reading of data from a special type of DVD.
- Blu-ray Disc - a high-density optical disc format for data and high-definition video. Can store 70 times as much information as a CD.
- BD-ROM Drive - a device used for reading data from a Blu-ray disc.
- BD Writer - a device used for both reading and writing data to and from a Blu-ray disc.
- HD DVD - a discontinued competitor to the Blu-ray format.
- Floppy disk - an outdated storage device consisting of a thin disk of a flexible magnetic storage medium. Used today mainly for loading RAID drivers.
- Iomega Zip drive - an outdated medium-capacity removable disk storage system, first introduced by Iomega in 1994.
- USB flash drive - a flash memory data storage device integrated with a USB interface, typically small, lightweight, removable, and rewritable. Capacities vary, from hundreds of megabytes (in the same ballpark as CDs) to tens of gigabytes (surpassing, at great expense, Blu-ray discs).
- Tape drive - a device that reads and writes data on a magnetic tape, used for long term storage and backups.
[edit]Secondary storage
Hardware that keeps data inside the computer for later use and remains persistent even when the computer has no power.
- Hard disk - for medium-term storage of data.
- Solid-state drive - a device similar to hard disk, but containing no moving parts and stores data in a digital format.
- RAID array controller - a device to manage several internal or external hard disks and optionally some peripherals in order to achieve performance or reliability improvement in what is called a RAID array.
[edit]Sound card
Enables the computer to output sound to audio devices, as well as accept input from a microphone. Most modern computers have sound cards built-in to the motherboard, though it is common for a user to install a separate sound card as an upgrade. Most sound cards, either built-in or added, have surround sound capabilities.
[edit]Other peripherals
In addition, hardware devices can include external components of a computer system. The following are either standard or very common.
Includes various input and output devices, usually external to the computer system.
[edit]Input
- Text input devices
- Pointing devices
- Mouse - a pointing device that detects two dimensional motion relative to its supporting surface.
- Optical Mouse - a newer technology that uses Light to track the surface under the mouse to determine the motion to be translated into cursor movements on the screen.
- Trackball - a pointing device consisting of an exposed protruding ball housed in a socket that detects rotation about two axes.
- Touchscreen
- Mouse - a pointing device that detects two dimensional motion relative to its supporting surface.
- Gaming devices
- Joystick - a general control device that consists of a handheld stick that pivots around one end, to detect angles in two or three dimensions.
- Gamepad - a general handheld game controller that relies on the digits (especially thumbs) to provide input.
- Game controller - a specific type of controller specialized for certain gaming purposes.
- Image, Video input devices
- Image scanner - a device that provides input by analyzing images, printed text, handwriting, or an object.
- Webcam - a low resolution video camera used to provide visual input that can be easily transferred over the internet.
- Audio input devices
- Microphone - an acoustic sensor that provides input by converting sound into electrical signals.
Service
Acts of services
- Administrative service, a part of the work load of university faculty
- Civil service, career employees of government
- Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community, or a punishment that may be imposed by a court
- Customer service, provision of assistance to customers or clients
- Table service
- Domestic service, employment in a residence
- Fan service, a Japanese term referring to something which is specifically designed to entertain fans
- Military service, a country's armed forces
- Public services, services carried out with the aim of providing a public good
- Selfless service, a service which is performed without any expectation of result or award.
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web, abbreviated as WWW and commonly known as the Web, is a systemof interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. With a web browser, one can viewweb pages that may contain text, images, videos, and other multimedia and navigate between them by using hyperlinks. Using concepts from earlier hypertext systems, British engineer and computer scientist Sir Tim Berners-Lee, now the Director of the World Wide Web Consortium, wrote a proposal in March 1989 for what would eventually become the World Wide Web.[1] He was later joined by Belgian computer scientist Robert Cailliau while both were working at CERNin Geneva, Switzerland. In 1990, they proposed using "HyperText [...] to link and access information of various kinds as a web of nodes in which the user can browse at will",[2] and released that web in December.[3]
"The World-Wide Web (W3) was developed to be a pool of human knowledge, which would allow collaborators in remote sites to share their ideas and all aspects of a common project." [4] If two projects are independently created, rather than have a central figure make the changes, the two bodies of information could form into one cohesive piece of work.
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine that receives input, stores and manipulates data, and provides output in a useful format.
Although mechanical examples of computers have existed through much of recorded human history, the first electronic computers were developed in the mid-20th century (1940–1945). These were the size of a large room, consuming as much power as several hundred modern personal computers (PCs).[1] Modern computers based on integrated circuits are millions to billions of times more capable than the early machines, and occupy a fraction of the space.[2]Simple computers are small enough to fit into small pocket devices, and can be powered by a small battery. Personal computers in their various forms are icons of the Information Age and are what most people think of as "computers". However, the embedded computers found in many devices from MP3 players to fighter aircraft and from toys to industrial robots are the most numerous.
The ability to store and execute lists of instructions called programs makes computers extremely versatile, distinguishing them from calculators. The Church–Turing thesis is a mathematical statement of this versatility: any computer with a certain minimum capability is, in principle, capable of performing the same tasks that any other computer can perform. Therefore computers ranging from a netbook to a supercomputer are all able to perform the same computational tasks, given enough time and storage capacity.
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from Latin: aurum, "shining dawn", hence adjective, aureate) and an atomic number of 79. It has been a highly sought-after precious metal for coinage, jewelry, and other arts since the beginning of recorded history. The metal occurs as nuggets or grains in rocks, in veins and in alluvial deposits. Gold is dense, soft, shiny and the most malleable and ductile pure metal known. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Gold is one of the coinage metals and has served as a symbol of wealth and a store of value throughout history. Gold standards have provided a basis for monetary policies. It also has been linked to a variety of symbolisms and ideologies.
A total of 161,000 tonnes of gold have been mined in human history, as of 2009.[1] This is roughly equivalent to 5.175 billion troy ounces or, in terms of volume, about 8,333 cubic meters, or a 20.274m x 20.274m x 20.274m block.
Although primarily used as a store of value, gold has many modern industrial uses includingdentistry and electronics. Gold has traditionally found use because of its good resistance tooxidative corrosion and excellent quality as a conductor of electricity.
Chemically, gold is a transition metal and can form trivalent and univalent cations in solutions. Compared with other metals, pure gold is chemically least reactive, but it is attacked by aqua regia (a mixture of acids), forming chloroauric acid, but not by the individual acids, and by alkaline solutions of cyanide. Gold dissolves in mercury, forming amalgam alloys, but does not react with it. Gold is insoluble in nitric acid, which dissolves silver and base metals. This property is exploited in the gold refining technique known as "inquartation and parting". Nitric acid has long been used to confirm the presence of gold in items, and this is the origin of the colloquial term "acid test", referring to a gold standard test for genuine value.
